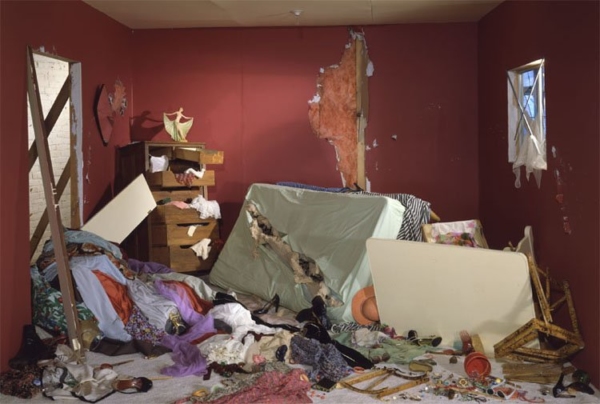
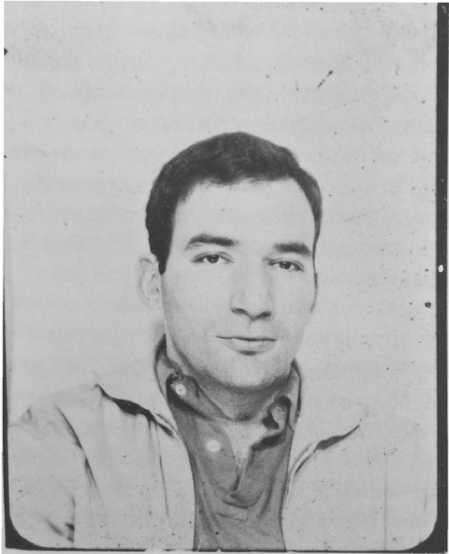
Complexity enchants ANT, new materialism, posthumanism, media studies, affect theory, and the literary undertakings of postcritique, new descriptivism, and “weak theory.” Its prophets claim as virtue that reality is immanent to itself, that no individual element of a complex web can be said to activate “a more fundamental reality” than any other. There is therefore a propulsive purpose accorded to critics: count up the everything, trace out the complexities, caress nuance, feel the vibe, what is connected to what. When everything is complicated and criticism calls itself to the tasks of phenomenological witnessing and empiricist tabulating, the vocation of criticism to make a cut in the swath of experience, to shift registers to a different order of knowing, is abandoned.