This Cannot Be Real: “Art and Objecthood” at 50
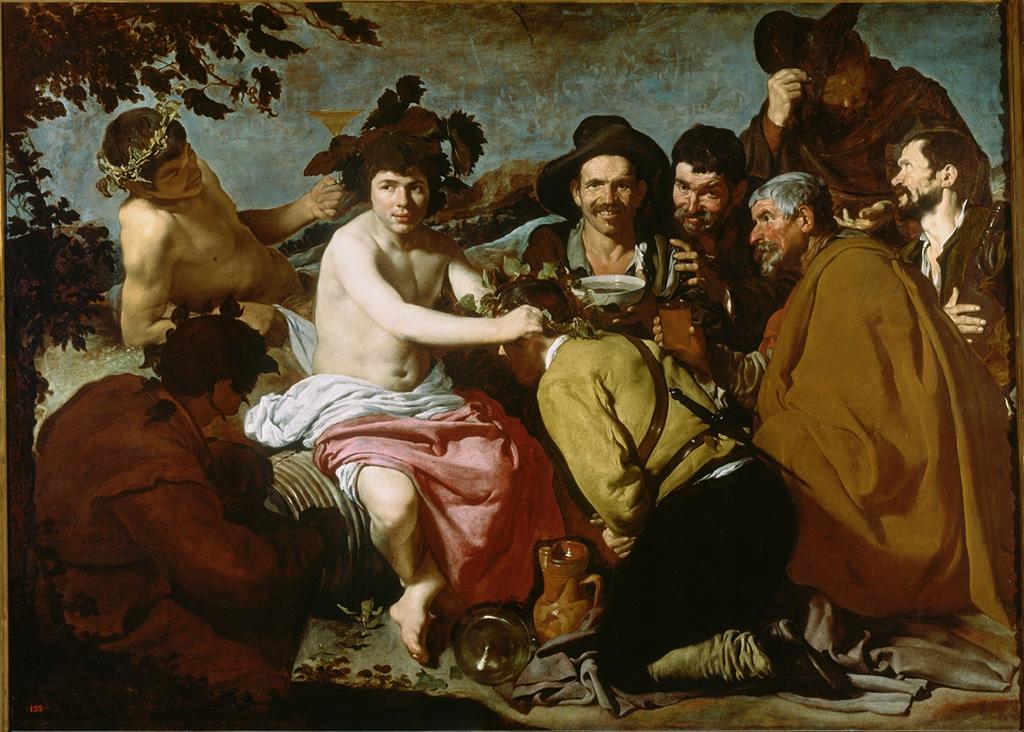
It’s important to note that the word “conviction,” Fried’s keyword for the effect produced by the successful painting, is an ambivalent term in his criticism. Sometimes the word refers to a judgment of value, or quality, defined loosely as the capacity of a given work to stand comparison with valued earlier masterpieces. But in “Art and Objecthood,” and at other key moments in his criticism—“Caro’s Abstractness,” for instance—“conviction” refers to the specific experience of the suspension of objecthood.