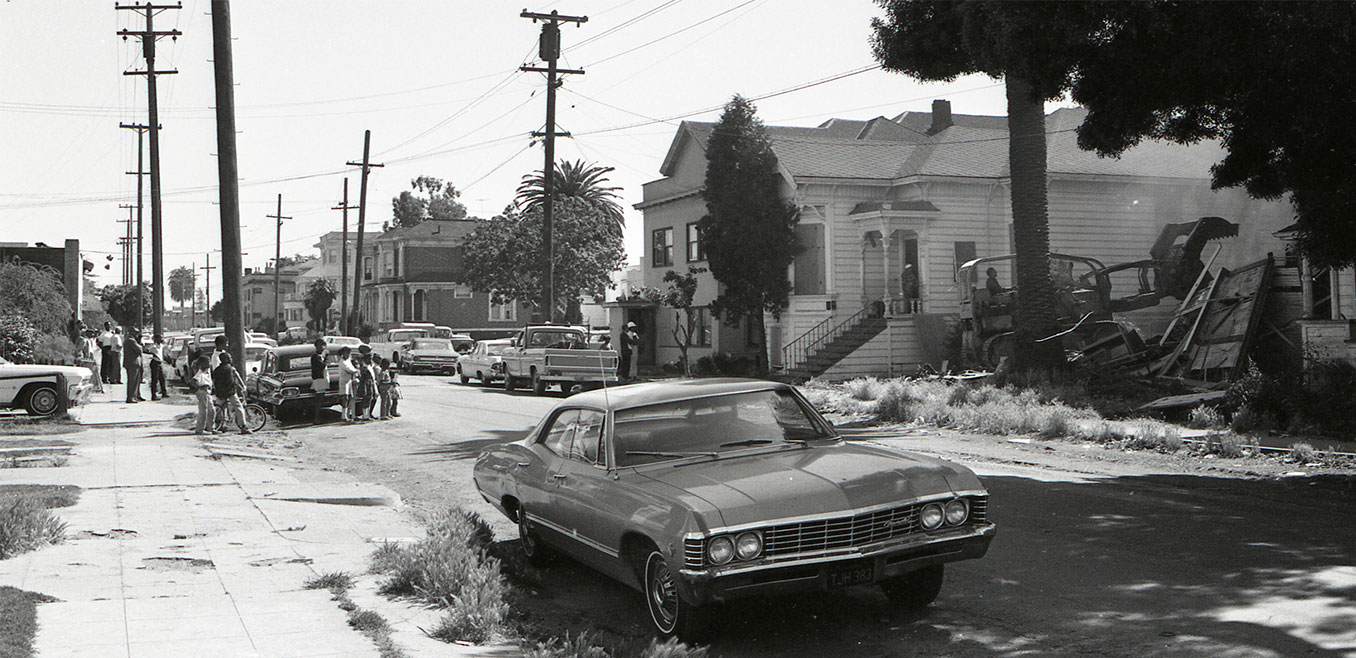
The benefits that black professionals received from new urban renewal was less a change in how they define their interests than a change in opportunities to pursue those interests. There has been an underappreciation for the role of class interests in driving black housing professionals and property owners’ politics during the postwar urban renewal period.
BY Anton Jäger
Bullshit Jobs is one long exercise in evasion—an attempt to go “beyond” capitalism without actually going through it. Graeber prefers the muteness and aphasia of the animal over the interdependence of the speaking subject. Yet as Marx, Engels and contemporaries already recognized, Kant’s ape has to begin to speak and assume his role as a member of coercive communities if history is to ever start.
Granger and the League’s promotion of trade unionism as a vehicle for civil rights highlights the problem with the commonplace disposition to view the NUL and NAACP through dichotomous lenses like Bookerite or Du Boisian. Such frameworks not only look past institutional politics’ sway over the scope of these civic groups’ agendas, but they may also obscure the influence of changes in the broader political landscape over the parameters of African American civil rights.
I wonder and worry if the fashionability of the field comes from its evasion of this question. Does it spring from a hope…that capital and capitalists can regulate themselves, that in effect, capitalism can have a history sans class politics. As Stein’s work shows, this seems at best naively decontextualized—detached from the actual history of capitalism. And at worst? Then the new history of capitalism looks a lot like the ideological expression of its subject.
BY Anton Jäger
The reason that contemporary liberal writers seem to have such thorough problems with the form of anti-racism exemplified by the Populist movement, is not, therefore, that Populists sought to unite poor white and black tenants in their shared “material self-interest.” Rather, it lies in the fact that they did so without seeing such co-operation as originating in a moral duty, and refused to carry out the necessary amount of affective investment.
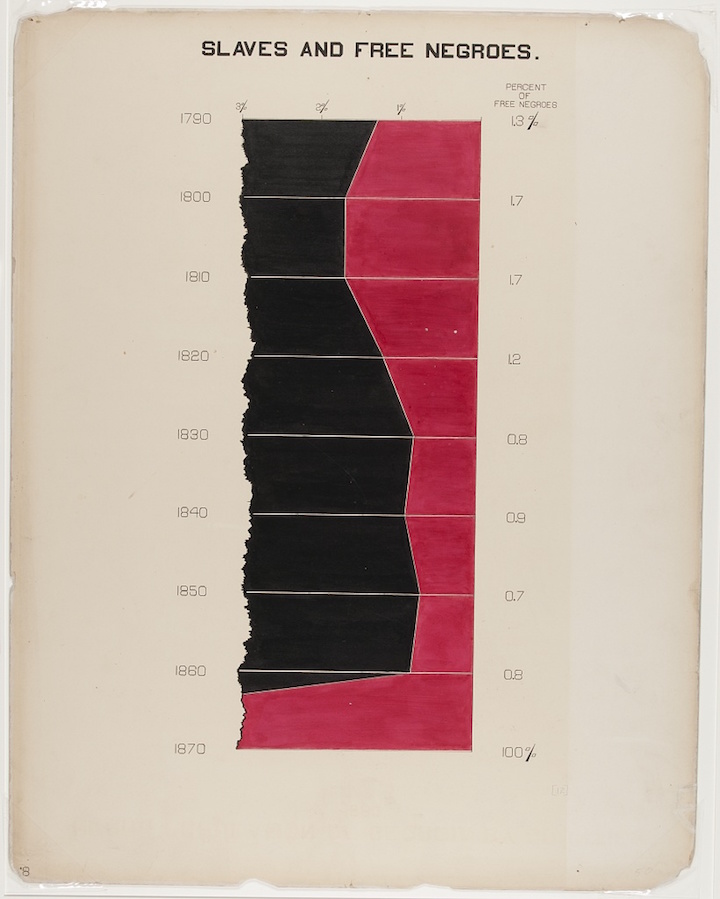
BY James Oakes
Despite his longstanding socialist sympathies, DuBois was repelled by the specter of revolutionary violence, hence his admiring account of the moderation of the southern slaves. They “showed no disposition to strike the one terrible blow which brought black men freedom in Haiti…. for the simple reason that there was an easier way involving freedom with less risk.” They went on strike.
There is no singular, transhistorical “Black Liberation Struggle” or “Black Freedom Movement,” and there never has been. Black Americans have engaged in many different forms of political expression in many different domains, around many different issues, both those considered racial and not. They have engaged in race-solidaristic formations and in close concert with others, in class-based and multiclass alliances.
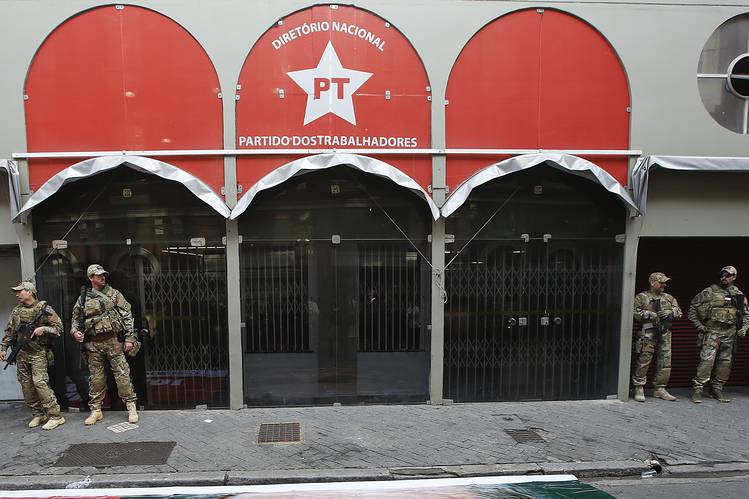
The neoliberal program includes: a) the drastic reduction of the federal budget, with a direct impact on social welfare, education, public health, and research spending, a.k.a. “the death budget”; b) labor legislation reform, removing or weakening many of the longstanding protections enjoyed by Brazilian workers and, under the guise of creating “flexible” labor relations, undermining the country’s trade-union movement; and c) social security reform, imposing stricter and longer work requirements, which, given the current and past employment structure would make full retirement unattainable for large sectors of Brazil’s working class.
BY Jan Sowa
There is, finally, one more reason why only a unified front of Old and New Left may be successful in countering both neoliberalism and populism within parliamentary politics. An important—I’d say even the largest—part of progressive political mobilization is nowadays done by women. At least that is the situation in Poland. It is obvious that women would not give up women’s causes and fight just for redistribution under the banners of the Old Left. We do not need, however, to treat this as a limitation or predicament. As a matter of fact, the women’s struggle is undoubtedly the biggest and the most important single positive factor in contemporary Polish politics, a fact that was very well epitomized in autumn 2016 by the so called Black March and women’s strike in opposition to the possibility of further restrictions on a Polish abortion law that is already one of the most restrictive in the EU.
To lay out, as clearly and as programmatically as we could, the reasons why despite protestations to the contrary, antiracism, understood as insisting on the symmetry of fighting discrimination and fighting exploitation, suppresses the development of a working class politics rather than offering a road to it. To make this point, the essays printed here, perhaps a little more insistently than our previous responses to critics, attend to the way that antiracism is an expression of the class position of those of us who produce the bulk of the commentary on injustice, and who routinely confront race and gender disparities in our everyday lives.